This article explains the different types of brake systems, their mechanisms of operation, and regenerative braking systems for efficient driving experience.
Brake systems are a basic part of any vehicle, assuming a vital role in guaranteeing your well-being and control while driving. Whether you are driving a vehicle, truck, cruiser, or even a bike, a well-efficient brake mechanism is fundamental for deceleration and halting. We perceive the meaning of a very much kept-up hydraulic and automated brake mechanism in improving the driving experience as well as, more significantly, in ensuring the security of drivers and travelers.
Complexity of brake assist systems
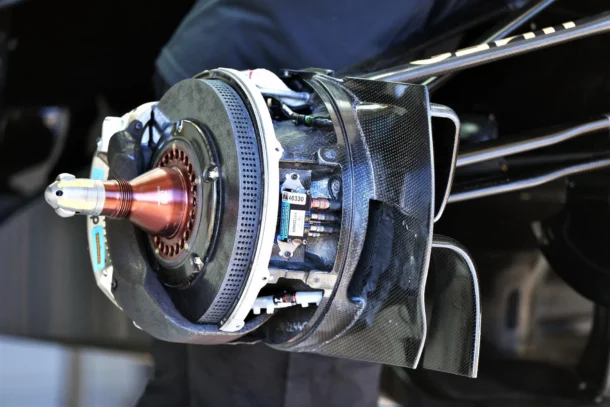
Source: motortrend.com
Brake discs are one of the essential parts of a braking mechanism in the brake circle, it is also known as the brake rotor. Brake discs are regularly made of solid metal or composite materials and are joined to the wheel center. At the point when the brakes are applied, brake cushions clip onto the rotating discs, creating erosion that slows down and at last stops the vehicle.
Brake pads are crucial components that connect with the brake systems rotors during the braking process. These pads are ordinarily made of composite materials containing friction materials like carbon, ceramic, and metallic compounds. The capacity of brake pads to endure intensity and grating is crucial for powerful braking performance.
Brake calipers house the brake pads and assume a significant part in the braking process. At the point when the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is applied to the calipers, making them crush the brake pads against the rotating brake discs. This friction produces the essential force needed to stop the vehicle.
Types of brake systems
Disc brakes are generally utilized in current vehicles and deal predominantly with brake execution. As referenced before, they consist of brake discs, brake pads, and calipers. The open design of disc brakes works with powerful intensity scattering, preventing overheating during prolonged use.
Drum brakes are as yet utilized in certain applications, particularly in the back tires. Drum braking mechanisms comprise brake drums, brake shoes, wheel cylinders, and springs. At the point when the brake pedal is squeezed, brake shoes extend against the inside surface of the drum, creating rubbing and slowing down the vehicle.
Anti-lock brake systems (ABS) are a security highlight intended to forestall wheel lock-up during heavy braking, particularly in crisis circumstances. ABS sensors monitor wheel speed, and on the off chance that a wheel is nearly secured, the framework modulates brake pressure, permitting the wheel to maintain traction with the road. This upgrade directs control and diminishes the risk of sliding.
Electronic brake-force distribution (EBD) is an innovation that ideally distributes braking force among the wheels to regulate vehicle load and street conditions. This guarantees that each wheel gets the proper measure of braking force, further developing strength and control during braking.
Brake system control module
The essential rule behind braking mechanisms is the change of active energy into nuclear power through friction. At the point when the brakes are applied, the brake pads create friction against the rotating brake discs. This friction produces heat, which should be effectively dissipated to forestall brake fade and keep up with the ideal performance of your vehicle’s brake systems.
Hydraulic pressure is a critical factor in transmitting force from the brake pedal to the brake parts. The brake master cylinder, associated with the brake pedal, compresses the brake liquid. This strain is then communicated through the brake lines to the brake calipers or wheel chambers, bringing about the pressure of brake pads or shoes against the braking surface.
Brake fade happens when excessive intensity develops in the braking mechanism, prompting a transitory decrease in braking proficiency. This peculiarity can result from delayed and forceful slowing down, and it highlights the significance of braking system design and materials fit for managing heat effectively.
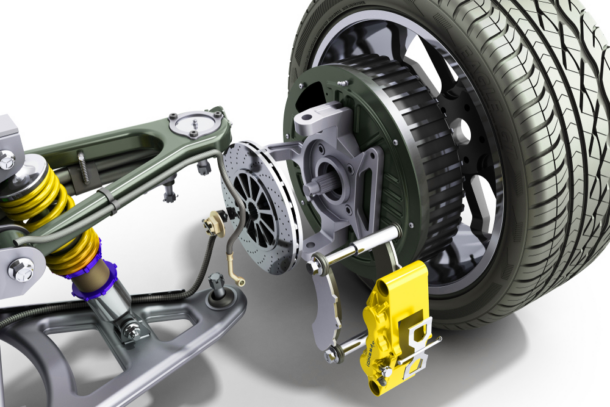
Hydraulic brake systems

Source: psbrake.com
Brake fluid transmits force inside the hydraulic brake mechanism, guaranteeing steady and dependable brake execution. Master cylinders, brake lines, and brake chambers form the whole hydraulic brake system, assuming a key part in transmitting the brake force.
Brake lines act as courses for brake fluid, sending hydraulic tension from the master chamber to the brake calipers. Brake fluids are commonly glycol-based, an incompressible fluid that guarantees a reliable exchange of power from the brake pedal to the brake parts. Standard support of brake fluid is vital to preventing brake system breakdowns.
Regenerative braking to elevate the driving experience
Some modern vehicles, particularly electric and hybrid cars, use regenerative braking. In this framework, the electric engine acts as a generator during braking, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This energy is then put away in the vehicle’s battery for later use, working on general effectiveness.
Brake-by-wire frameworks further provide electronic control by wiping out the direct mechanical connection between the brake pedal and the brakes. The electronic signals from the pedal are interpreted by a control unit, which then changes the braking force accordingly. This innovation gives greater adaptability in advancing brake systems and coordinating with vehicle security frameworks.
Automotive brake technology
Brake technology has advanced altogether throughout the long term, introducing developments with improved execution, security, and durability.
Electro-hydraulic brakes incorporate electronic control with hydraulic actuation. This takes into account more exact control of braking force and enables highlights like brake-by-wire, where the mechanical connection between the brake pedal and the brakes is replaced by electronic transmissions.
Automated emergency braking (AEB) is a high-level safety feature that utilizes sensors, cameras, and radar to identify potential collisions. If the framework verifies that a collision is imminent and the driver does not answer, it can naturally apply the brakes to forestall or moderate the effect.
Carbon-ceramic brakes are used in high-performance and extravagant vehicles. These brakes utilize lightweight and heat-resistant materials, giving better execution, reduced weight, and improved heat dissipation in contrast with traditional brake systems.
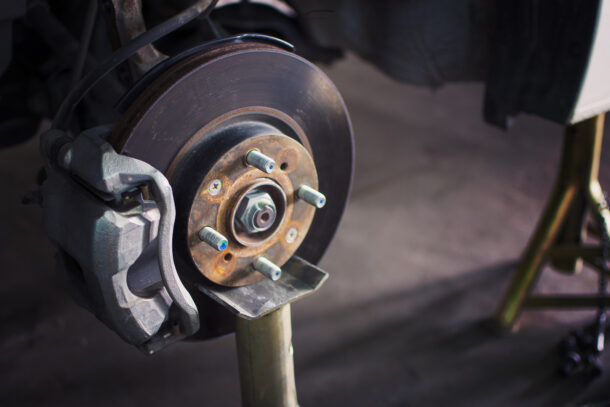
Brake system failures

Source: shur-wayautobody.com
Brake noise can be disruptive and demonstrates possible issues with the brake parts. Recognizing the causes, for example, broken pads or rotor damage, and tending to them promptly can prevent further damage.
Brake fade, the progressive decrease in braking power, can be brought about by overheating. Understanding prevention techniques, for example, downshifting on steep descents, is pivotal for keeping up with steady braking performance. Vibrations during braking can be credited to uneven brake pad wear or distorted rotors. A thorough inspection of brake systems, followed by fitting measures, for example, rotor resurfacing or replacement, can redress this issue.
Brake system fluid flushing
Brake fluids absorb moisture after some time, which can reduce braking productivity and erosion inside the braking mechanism. Periodic flushing and substitution of brake liquid are vital for keeping up with the hydraulic integrity of the framework.
Brake pads and rotors have a limited life expectancy and ought to be supplanted when they arrive at their wear limits. Ignoring broken-down brake parts can lessen braking execution, increase stopping distances, and potential safety hazards.
Routine assessments of the braking systems are fundamental for guaranteeing their ideal presentation and recognizing possible issues before they become serious issues. Checking brake cushions, plates, calipers, and fluid levels should be essential for regular maintenance.
Driving excellence with efficient brake system health
Brake mechanisms are central to vehicle security and control, and figuring out their types, components, and operation is pivotal for both drivers and automotive enthusiasts. As innovation keeps on propelling, braking mechanisms will probably see further advancements pointed toward enhanced execution, productivity, and overall safety on the road. The quality maintenance of braking system ensures the driving excellence of your vehicle. Whether it is the traditional hydraulic brake system or the cutting-edge electro-hydraulic brake-by-wire system framework, the development of brake systems mirrors the continuous obligation to make vehicles more secure and more dependable for everyone on the road.




