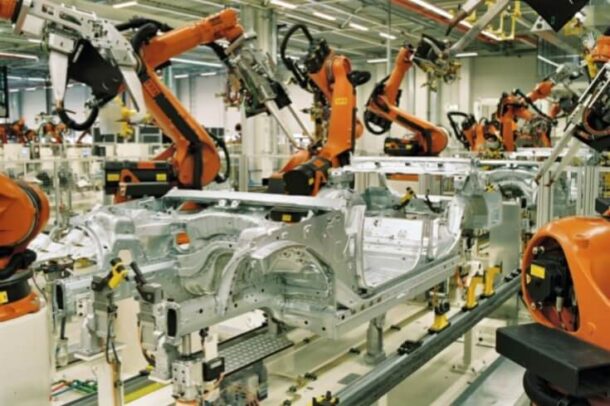
Automotive manufacturing is a complex process with a multitude of moving parts. Vehicle manufacturers are always looking for a way to streamline their process and linear actuators are a way to achieve this. Linear actuators are widely used in this industry to optimize everything from steering to braking, and even doors.
The best linear actuators provide manufacturers an easier route to perfection in automobile production. However, recognizing the best linear actuator is another ball game entirely. We’ll be discussing the top linear actuators in the automotive industry.
How Does a Linear Actuator Work?

Source: tolomatic.com
Linear actuators work by moving equipment in a straight line. It moves the piece accurately and repeatedly if required. Manufacturers use linear actuators in a system to assist in linearly moving a payload against a rotary one. Linear actuator prevents electric motors operating in rotary motion, as created. To do this, it convert it to a linear motion.
The motor is connected to the linear actuator using a belt or a flexible coupling, which enables the motor to be mounted perpendicular or axially to the linear actuator. A variety of motor sizes can also be mounted to the actuators depending on requirements.
Linear actuators incorporate linear bearings to support the moving payload. They enable rotary bearings to support the ball screw, lead screw, or belt pulleys. With this, they can operate as ‘solo’ devices. This makes them easier to mount into existing machines. It also eliminates the need to design or manufacture expensive custom parts.
A linear actuator system can be paired with the payload placed between them. They increase the load capacity and stability of a linear actuator system. However, a shaft or belt is often needed to keep the two actuators about each other.
Top 3 Linear Actuators Used in Automotive Manufacturing

Generally, they’re three types of linear actuators – Ball Screw Actuators, Lead Screw Actuators. and Belt Actuators. These linear actuators can produce motion in various methods required in automotive manufacturing.
1. Ball Screw Linear Actuator
This type of linear actuator operates with a high-precision nut and recirculating ball bearings. They rotates around a ground screw thread. In application, it’s quite similar to a standard ball race having the load transmitted by the rolling balls. The system offer high-precision and low friction as advantages. This is efficient in converting rotary to linear motion.
Stepper or servo motors are mostly used to supply rotary motion. Ball screw actuators are best for repeatable indexing and fast cyclic applications like machine tools, medical systems, and scientific instruments.
2. Belt Linear Actuators
Belt linear actuators work more like a system where a belt is placed between two pulleys, attached to the moving carriage, and as the belt rotates, the carriage which is pulled along the actuator. A motor is mounted perpendicular to the actuator to drive the pulleys. The whole system is coupled with a flexible coupling for efficiency.
One of the advantages of this linear actuator is that they provide a relatively low-cost alternative, as they naturally have a lower level of precision. Moreover, they’re recommended for long-distance travel and high linear speed applications like packaging and automated material handling systems.
3. Lead Screw Linear Actuator
Lead screw linear actuator uses a plain screw or nut arrangement in a motor to translate rotary motion from linear motion. An AC induction motor or a manually driven screw is the most common use method of supplying rotary motion, as they’re typically used in low-precision and low-cost applications.
The ability of the linear actuator to ‘back drive’ is, however, reduced over ball screw actuators due to the low efficiency of the screw or nut. Nevertheless, it can be a great advantage in some applications as it helps to keep the payload stationary while out of motion. They’re usually applied in manual lift systems and agricultural equipment, where reliability and safety are more important than precision and performance.
Components of a Linear Actuator
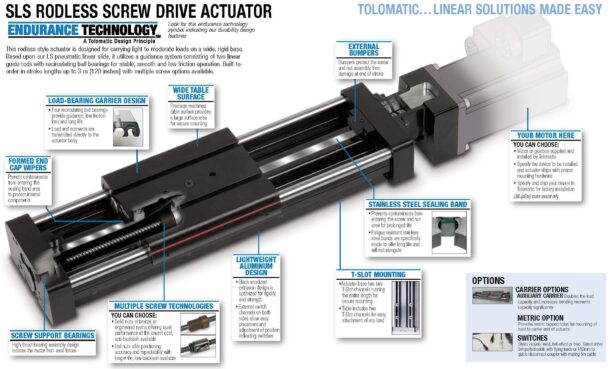
Source: tolomatic.com
1. Controller
The Controller enables efficiency in system function. It also allows an operator to add quantities and setpoints.
2. Power source
The AC or DC motor provides the energy essential for driving the actuator. Though electricity is the main energy source, fluid, and air energy is also used.
3. Power converter
The power converter transmits power from the source to the actuator with the help of measurements from the Controller.
4. Phase IndexTM Sensor
The phase Index sensor is a positioning sensor for electromechanical actuators. It is a high-speed, high-resolution, digital, and non-contact position sensor resistant to shock, vibrations, particulate debris, and moisture.
Conclusion
Linear actuators are machine components that transform rotational motion into accurate and smooth linear motion. The three main types of linear actuators are ball screw, belt, and lead screw linear actuators. While the bell screw linear actuators offer high precision and low friction in converting rotary to linear motion, the belt actuator is a low-cost alternative. In contrast, the lead screw linear actuators offer low precision but are a safer option.
However, each of these linear actuators offers one thing in common: to facilitate the precise positioning of components. They also help in lifting, lowering, pulling, and pushing motions. So it’s no surprise why linear actuators are such a popular technology in the automotive manufacturing industry.




